02 | Funded Project
The role of NKT cells in the endogenous anti-glioblastoma immune response initiated by CAR-NK cell therapy

Funding Period: 01.01.2026 – 31.12.2027
Project Leader: Dr. Michael Burger
University Cancer Center Frankfurt am Main
Project Description
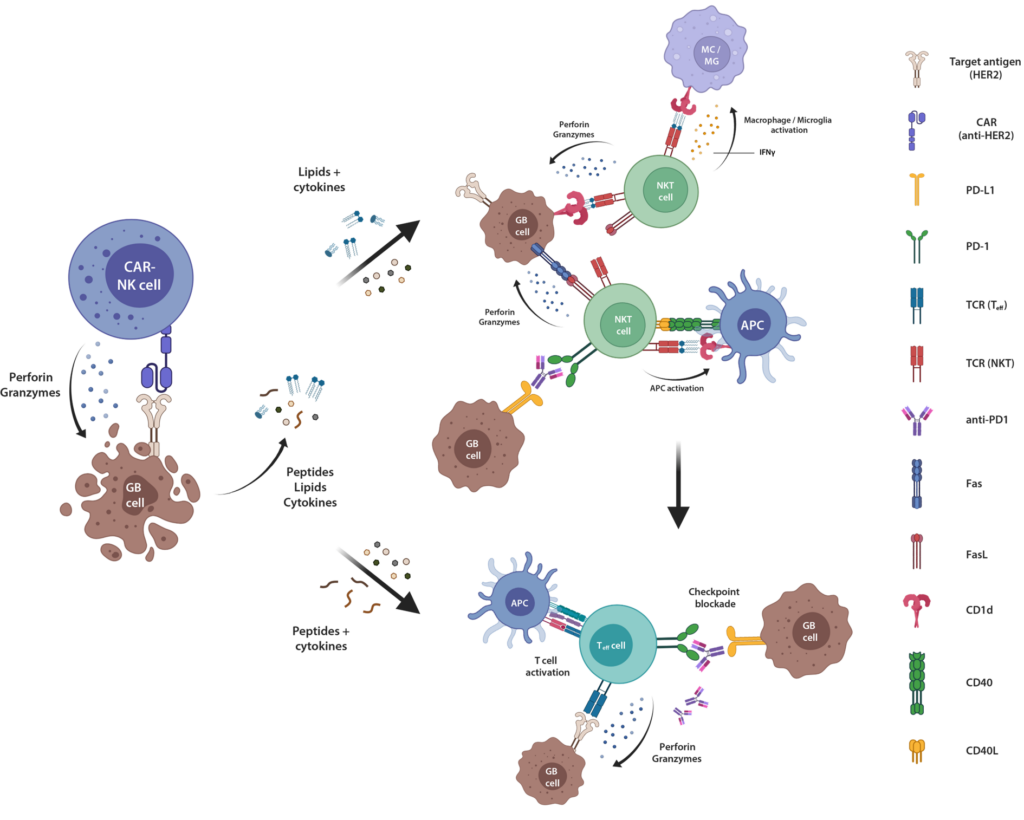
Glioblastoma cells inhibit the activity of the immune system by producing immunosuppressive molecules such as PD-1 ligand. During the previous funding period, we already have demonstrated that this mechanism, which is detrimental for glioblastoma therapy, can be overcome by infecting tumor cells with a viral system derived from human adeno-associated viruses (HER2-AAV). After infection of the tumor with HER2-AAVs, antibody fragments (so-called checkpoint inhibitors) are produced locally, releasing the blockade of the immune response. This significantly enhanced the effectiveness of natural killer cells targeted against glioblastoma cells (CAR-NK cells), due to an improvement of the endogenous immune response against glioblastoma cells triggered by CAR-NK cell therapy. This is an effect that is crucial for long-term tumor control.
Laboratory experiments hinted to an increase of natural killer T cells (NKT cells) by the combination therapy with checkpoint inhibition and CAR-NK cells. In the immune system, NKT cells are responsible for the defense against lipid antigens. We also observed an increase in NKT cells in tumor tissue derived from patients who were treated with the combination of CAR-NK cell therapy and a checkpoint inhibition as part of the ongoing CAR2BRAIN study.
In the current funding period, we therefore aim to investigate the role of NKT cells in the endogenous anti-tumor immune response induced by combination therapy with CAR-NK cells and checkpoint inhibition. First, the mechanisms leading to activation of NKT cells will be characterized in detail. Subsequently, strategies will be developed to enhance the desired anti-tumor activity of these cells (Fig. 1). The practical relevance of the laboratory findings for patients will additionally be assessed by analysing tumor material from study participants of the CAR2BRAIN trial.
The overarching goal of this research project is to improve the effectiveness of glioblastoma therapies through a rational combination of cellular immunotherapies and immunomodulators.
Funding of this project by the Anni Hofmann Foundation is therefore an important contribution to the development of innovative approaches for glioblastoma immunotherapies.